Introduction
Polymers: Macromolecules of high molecular weight which are formed by linkage between large numbers of small molecules called monomers.
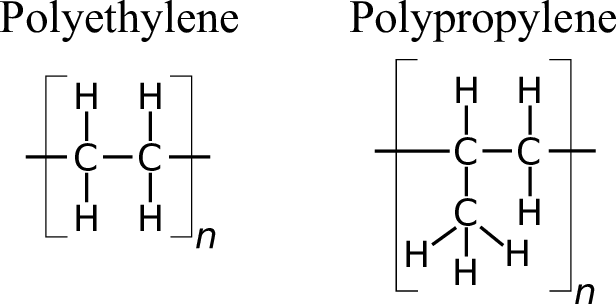
Eg: Ethylene + Ethylene + … = Polythene
Types #
Polymers can be classified in many different ways:
On the basis of source:
Natural: Starch, Cellulose, Natural Rubber, DNA, RNA
Synthetic: PE, PVC, PS
On the basis of repeating units:
Homopolymers: repeating monomer units are same.
Co-polymers: More than one type of monomers are present. Ex: Nylon 6,6, PEVA, ABS
Structure
Linear
Branched
3 dimensional
Cross-linked
On the basis of arrangement of functional groups, side chain or branches
Classification on the basis of tacticity
Isotactic
Syndiotactic: alternate arrangement
Atactic: randomly arranged
On the basis of molecular forces
They are linear long chain polymers which can be softened on heating and hardened on cooling.
Ex: PE, PP, PS
They have crosslinked 3D network which once hardened cannot be softened or reversed again.
Ex: Bakelite, Melamine, epoxy resin, polyester.
Elastomers are rubber like elastic polymers which can be stretched at least 3 times their original form.
Fibers
They are polymeric chains which are held by strong intermolecular forces like H bonding.
Eg: Starch, cellulose, Nylon
On the basis of synthesis
They are formed when the repeating units are added one by one to the main chain.
Most of the times they are formed by free radical/cationic/anionic form.
Monomers always have one or more double bonds
2 different types of monomeric units react through their functional groups and combine together.
Elimination of strong molecule like water, ammonia.
Ex: Nylon 6,6
PDI: polydispersity index: Mₘ/Mₙ