Lasers (contd)
Metastable state #
- Required for population inversion
- Has a longer lifetime $10^{-6} \rightarrow 10^{-3}s$
- Created between the energy levels where we want to control and hold the atoms.
- We do stimulated emission of atoms at the metastable state.
Pumping mechanisms for population inversion #
- Optical pumping
- Light is used for stimulated absorption.
- Used in solid lasers.
- Eg: Ruby, Nd:YAG, Nd:Glass lasers
- Electrical discharge pumping
- Used in gas lasers.
- Eg: He-Ne, CO2, Argon ion laser
- Chemical pumping
- . Excitation due to chemical excitation
- Eg: HF, DF lasers
- Injection current pumping
- Used in semiconductors
- Injection of current through junction causes inversion among minority charge carriers
- Eg: InP, GaAs.
Laser system #
- Active medium: contains atoms to be excited
- Optical cavity: Two mirrors for reflection and constructive interference for amplification.
- Pumping mechanism: Used to excite atoms
3 level laser system #
Let there be three energy levels $E_0<E_1<E_2$
- Pumping from $E_0 \rightarrow E_2$
- $E_2\rightarrow E_1$ metastable state
- Population inversion is achived between $E_0$ and $E_1$
- Lasing action $E_1\rightarrow E_0$
4 level laser system #
Let there be four energy levels $E_0<E_1<E_2<E_3$
- Pumping from $E_0 \rightarrow E_3$
- Rapid decay from $E_3 \rightarrow E_2$
- Population inversion is achived between $E_1$ and $E_2$
- Stimulated lasing action $E_2\rightarrow E_1$
- Gets back to the ground state $E_1\rightarrow E_0$
Various Lasers #
He-Ne laser #
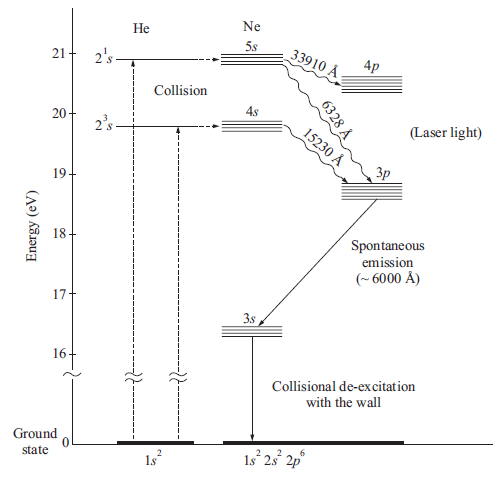
- Helium gets excited by electron collision
- Neon gets excited due to collision with He.
- He:Ne=10:1
Merits #
- Operated continuously
- Highly monochromatic
- Highly stable
- Output can be tuned to any certain available λ
- Separate cooling isn’t needed
Demerits #
Very low compared to lasers such as a ruby laser.
Applications #
- Holograms
- Industries
- Communication
- Printers
- Laboratories
- Scanners
Semiconductor laser #
ND:YAG laser #
Applications of lasers #
- Communication
- Optical communication
- LIDAR: light detection and ranging
- High speed photography
- Holography
- Medical application
- Cancer treatment
- Surgeries
- Industrial
- Cutting, Welding, Drilling
- Electronics
- Scientific research
- Spectroscopy
- Photochemistry
- Non-linear optics
- Laser induced nuclear fusion